The Next Frontier for mRNA Could Be Healing Damaged Organs
2 min readThe Next Frontier for mRNA Could Be Healing Damaged Organs
In recent years, mRNA technology has gained significant attention for its role in developing COVID-19 vaccines. However,...
The Next Frontier for mRNA Could Be Healing Damaged Organs
In recent years, mRNA technology has gained significant attention for its role in developing COVID-19 vaccines. However, scientists are now exploring another exciting application for mRNA: healing damaged organs.
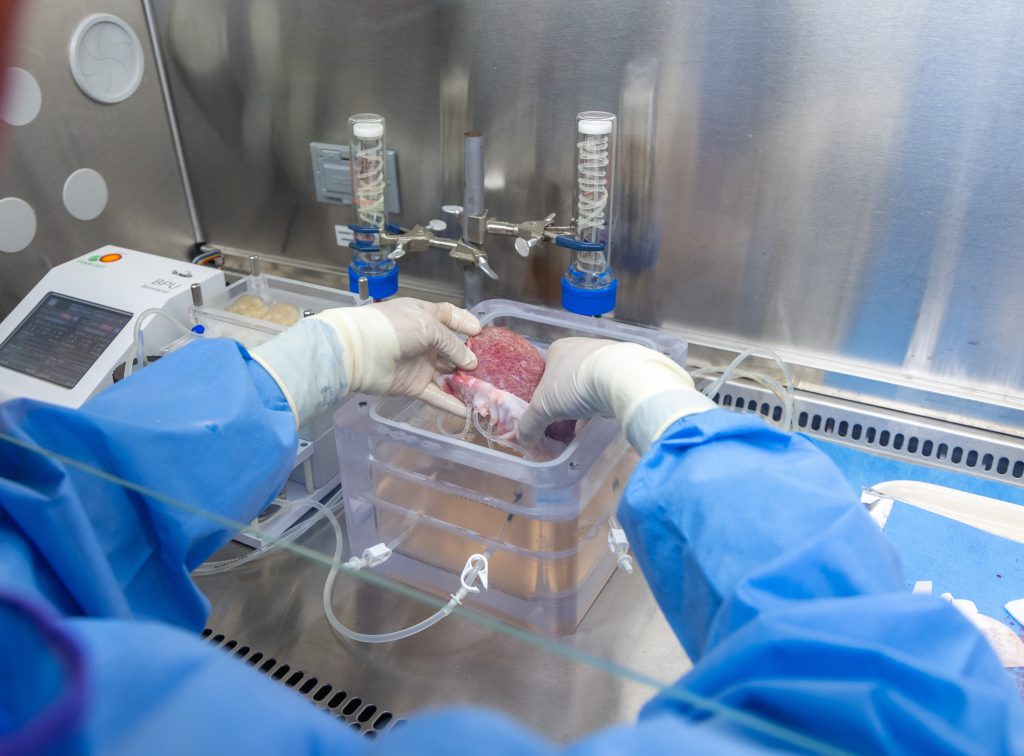
One potential use of mRNA technology is in regenerative medicine, where it can be used to stimulate the growth and repair of damaged tissues and organs. This could revolutionize the treatment of a wide range of conditions, from heart disease to spinal cord injuries.
By delivering specific mRNA sequences to targeted cells, researchers believe they can kickstart the body’s natural healing processes and promote tissue regeneration. This approach could offer new hope to patients with chronic conditions that have limited treatment options.
Moreover, mRNA therapy holds the promise of being a more precise and efficient way to repair damaged organs compared to traditional methods. With its ability to be tailored to specific cell types and functions, mRNA could potentially avoid the risks and side effects associated with other treatments.
While there is still much research to be done, the potential for mRNA to heal damaged organs is a promising step forward in the field of regenerative medicine. As scientists continue to unlock the full potential of this technology, we may soon see a future where organ repair is no longer a distant dream, but a reality.
In conclusion, the next frontier for mRNA could be in healing damaged organs, offering new possibilities for patients suffering from a variety of conditions. With continued research and innovation, we may soon witness a new era of regenerative medicine powered by the remarkable capabilities of mRNA.




